Insulated Siding Key to Energy-Efficient Homes – Insulated Siding: Key to Energy-Efficient Homes – Thinking about upgrading your home’s exterior? Beyond just aesthetics, insulated siding offers a powerful punch to your energy bills and overall comfort. We’re diving deep into the world of energy-efficient homes, exploring the different types of insulated siding, their installation, and the impressive long-term benefits they bring. Get ready to discover how this simple upgrade can transform your home and your wallet!
From vinyl’s versatility to fiber cement’s durability and metal’s modern appeal, we’ll break down the pros and cons of each material, comparing their thermal performance and helping you choose the perfect fit for your home’s style and budget. We’ll also tackle the installation process, maintenance tips, and even calculate the potential return on investment (ROI) – proving that energy efficiency doesn’t have to break the bank.
Prepare to be amazed by the impact insulated siding can have on your home’s energy consumption, environmental footprint, and overall curb appeal.
Introduction to Insulated Siding
Insulated siding is a game-changer in home construction and renovation, offering a compelling blend of aesthetic appeal and energy efficiency. Unlike traditional siding that relies on separate insulation, insulated siding integrates insulation directly into the siding panel itself, creating a more streamlined and effective thermal barrier. This innovative approach leads to significant energy savings and improved comfort levels within the home.Insulated siding typically consists of an outer layer of weather-resistant material, a core layer of insulation, and sometimes a backing layer for added strength and moisture protection.
The outer layer is what you see and determines the aesthetic of your home, while the insulation core provides the energy-saving benefits. The specific materials and their arrangement vary depending on the type of siding chosen.
Types of Insulated Siding
The choice of insulated siding depends on several factors including budget, desired aesthetic, and climate. Several popular options exist, each with its own unique properties.
- Vinyl Insulated Siding: Vinyl is a popular choice due to its affordability, low maintenance, and wide range of colors and styles. The insulation core is typically made of foam, such as polyisocyanurate (polyiso) or extruded polystyrene (XPS). Vinyl siding offers good thermal performance, but it’s generally not as durable as other options.
- Fiber Cement Insulated Siding: Fiber cement combines cement, cellulose fibers, and other additives to create a durable and fire-resistant siding. It offers superior longevity and weather resistance compared to vinyl, but it’s more expensive. Insulation cores in fiber cement siding often utilize foam materials similar to vinyl siding, contributing to its energy-efficient properties. It’s a popular choice for those seeking a more robust and long-lasting solution.
- Metal Insulated Siding: Metal insulated siding, often made of aluminum or steel, is exceptionally durable and resistant to fire, insects, and rot. The insulation core is usually a rigid foam, providing excellent thermal performance. However, metal siding can be more expensive than vinyl or fiber cement and may require more specialized installation.
Thermal Performance Comparison of Insulated Siding
The thermal performance of insulated siding is measured by its R-value, which indicates the material’s resistance to heat flow. A higher R-value means better insulation. While the exact R-value varies depending on the thickness and type of insulation used, generally, insulated siding offers significantly higher R-values compared to traditional siding with separate insulation. For instance, a typical 1-inch thick insulated vinyl siding might have an R-value of 4 or higher, whereas the same thickness of uninsulated vinyl siding would have an R-value close to zero.
Fiber cement and metal insulated siding often achieve even higher R-values due to the use of thicker insulation cores and potentially more effective insulation materials. The precise R-value should always be verified from the manufacturer’s specifications.
Energy Efficiency Benefits

Insulated siding offers a significant upgrade to your home’s energy performance, translating to tangible savings and enhanced comfort. By acting as a thermal barrier, it significantly reduces the amount of heat transferred between the inside and outside of your home, regardless of the season. This translates to lower energy bills and a more consistently comfortable living environment.
Browse the implementation of Insulated Siding for Noise Reduction: A Quieter Life in real-world situations to understand its applications.
Insulated siding works by creating an extra layer of insulation between your home’s exterior and interior walls. This layer prevents heat from escaping in winter and reduces heat absorption in summer. The effectiveness of this insulation is measured by its R-value, a higher R-value indicating better insulation properties. The material itself, often including foam or fiber-reinforced panels, traps air pockets which are poor conductors of heat.
This air barrier effectively slows down the rate of heat transfer, minimizing energy loss through your walls.
Impact on Energy Bills
The reduction in heat transfer directly impacts your energy consumption and, consequently, your energy bills. By minimizing the amount of energy needed to heat your home in winter and cool it in summer, insulated siding can lead to substantial savings over time. The exact amount saved will vary depending on factors such as your home’s size, climate, and existing insulation levels.
However, many homeowners report a noticeable decrease in their monthly utility costs after installing insulated siding. For example, a family in a typical suburban home might see a reduction of $300-$500 annually on their heating and cooling bills after installation.
Improved Indoor Comfort
Beyond the financial benefits, insulated siding contributes to a more comfortable living environment. It helps maintain a more consistent indoor temperature throughout the year, minimizing temperature fluctuations caused by external weather changes. This means fewer drafts, less temperature variation between rooms, and a more pleasant and stable indoor climate. Imagine a home where you feel consistently comfortable without constantly adjusting the thermostat—that’s the power of insulated siding.
This is particularly beneficial for families with young children or elderly individuals who are more sensitive to temperature changes.
Energy Savings Comparison
The following table illustrates the potential energy savings achievable with insulated siding, using hypothetical data based on average energy consumption patterns:
| Siding Type | R-Value | Annual Energy Savings ($) | Percentage Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Vinyl Siding | 0 | $0 | 0% |
| Insulated Vinyl Siding | 5 | $350 | 15% |
| Insulated Fiber Cement Siding | 7 | $500 | 22% |
| High-Performance Insulated Siding | 10 | $700 | 30% |
Installation and Maintenance
Insulated siding installation is a significant undertaking, impacting both the aesthetics and energy efficiency of your home. Proper installation ensures longevity and optimal performance, while regular maintenance prevents costly repairs down the line. Understanding the process and necessary upkeep is crucial for maximizing your investment.
Insulated Siding Installation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Successful insulated siding installation requires careful planning and execution. The following steps provide a general overview; always consult the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific siding type. Variations in techniques exist depending on the type of siding (e.g., vinyl, fiber cement, etc.).
- Preparation: Begin by thoroughly cleaning the existing exterior walls, removing any loose paint, debris, or damaged sections. Ensure the surface is dry and level. This step is critical for proper adhesion and prevents future problems.
- Framing and Sheathing (if necessary): If installing over existing siding, inspect for damage and address any issues. New construction might require installing sheathing for proper support. Ensure proper ventilation is maintained behind the siding.
- Installation of Furring Strips (Optional but Recommended): Furring strips create an air gap between the wall and the siding, improving insulation and ventilation. They are typically spaced according to manufacturer specifications.
- Siding Installation: Start at a corner or a prominent point, following the manufacturer’s instructions for overlapping and fastening. Use appropriate fasteners for your siding material. Ensure proper alignment and spacing between panels.
- Finishing Touches: Install trim, flashing, and other accessories as needed to complete the project. Caulk all seams and joints to prevent water infiltration.
Potential Installation Challenges and Solutions
Several challenges can arise during insulated siding installation. Foresight and planning are key to mitigating potential problems.
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Uneven Wall Surfaces | Use furring strips to create a level surface for the siding. |
| Difficult-to-Reach Areas | Employ scaffolding or extendable tools for safe and efficient installation. |
| Improper Fastening | Use the correct fasteners and follow manufacturer recommendations for spacing and depth. Over-fastening can damage the siding. |
| Water Infiltration | Ensure proper flashing and caulking around windows, doors, and other openings. |
Insulated Siding Maintenance: A Type-Specific Approach
Regular maintenance extends the life of your insulated siding and maintains its aesthetic appeal. The specific maintenance requirements vary depending on the siding material.
Vinyl Insulated Siding Maintenance
Vinyl siding is relatively low-maintenance. Regular cleaning with soap and water is usually sufficient. Avoid abrasive cleaners that could scratch the surface. Inspect for any damage and repair promptly to prevent further deterioration. A pressure washer can be used, but be cautious to avoid damaging the siding.
Fiber Cement Insulated Siding Maintenance
Fiber cement siding is more durable than vinyl but requires more maintenance. Regular cleaning is essential, and repainting might be needed every few years depending on environmental factors and exposure to the elements. Inspect for cracks or damage and repair as needed.
Tools and Materials for Insulated Siding Installation
A comprehensive list of tools and materials is crucial for a successful installation. This list isn’t exhaustive, and specific needs will vary depending on the project’s scope and the siding type.
- Measuring Tape
- Level
- Circular Saw or Hand Saw
- Drill with appropriate bits
- Caulk Gun
- Safety Glasses and Gloves
- Insulated Siding Panels
- Fasteners (nails, screws)
- Flashing and Trim
- Caulk
Cost-Effectiveness and ROI

Investing in insulated siding might seem like a significant upfront expense, but the long-term benefits in energy savings and increased home value often make it a worthwhile investment. Let’s delve into the cost-effectiveness and return on investment (ROI) you can expect.While the initial cost of insulated siding is higher than traditional vinyl or wood siding, the energy efficiency gains significantly offset this over time.
This makes it a smart financial decision for homeowners focused on both comfort and long-term savings.
Comparison of Initial Costs
Insulated siding typically costs more upfront than other exterior cladding options like vinyl or fiber cement. However, this higher initial investment is balanced by the substantial energy savings it provides. For instance, a typical 1,500 square foot home might see an increase of $5,000-$10,000 in initial costs compared to vinyl siding, depending on the chosen material and labor costs in the specific region.
Fiber cement siding often falls somewhere in between vinyl and insulated siding in terms of initial cost. The precise price difference will vary based on factors such as the home’s size, the complexity of the installation, and the specific materials used.
Long-Term Cost Savings Through Reduced Energy Consumption
The real value of insulated siding lies in its ability to significantly reduce energy consumption. By creating an effective thermal barrier, it minimizes heat transfer, leading to lower heating and cooling bills. This translates to substantial long-term savings. For example, a homeowner in a climate with significant temperature fluctuations might see a reduction of 15-25% in their annual energy bills.
This translates to hundreds or even thousands of dollars saved annually, depending on the size of the house and the climate. These savings accumulate over the lifespan of the siding, often exceeding the initial cost difference compared to less efficient options.
Return on Investment (ROI) Calculation for Insulated Siding
Calculating the ROI for insulated siding involves comparing the initial investment cost against the cumulative energy savings over a defined period. A simplified calculation can be performed as follows:
ROI = (Total Energy Savings – Initial Investment Cost) / Initial Investment Cost – 100%
For example, if the initial investment is $10,000 and the annual energy savings are $1,500, the ROI over 10 years would be:
ROI = ($15,000 – $10,000) / $10,000 – 100% = 50%
This calculation is a simplification. A more comprehensive analysis would factor in the lifespan of the siding, potential increases in energy costs, and the potential increase in home value.
Factors Influencing the Overall Cost of Insulated Siding Installation
Several factors contribute to the overall cost of insulated siding installation. Understanding these factors can help homeowners budget effectively.
- Home size and complexity: Larger homes and those with intricate architectural details will naturally require more materials and labor, increasing the overall cost.
- Type of siding: Different types of insulated siding, such as foam-backed vinyl or fiber cement, have varying material costs.
- Labor costs: Labor rates vary significantly by geographic location and the contractor’s experience.
- Material costs: Fluctuations in the cost of raw materials can impact the final price.
- Preparation and repair work: Existing siding removal, underlying wall repair, and other necessary preparation work can add significant expense.
- Permits and inspections: Obtaining necessary permits and scheduling inspections will incur additional fees.
Environmental Impact: Insulated Siding Key To Energy-Efficient Homes
Insulated siding offers a compelling environmental advantage by significantly reducing a home’s energy consumption. This translates to a lower carbon footprint and a smaller demand on natural resources, contributing to a more sustainable built environment. By improving a building’s thermal performance, insulated siding directly addresses the environmental impact of energy production and consumption.The environmental benefits extend beyond just energy savings.
The choice of siding material itself plays a crucial role in the overall sustainability equation. Understanding the lifecycle impacts of different materials, from manufacturing to disposal, is key to making informed, eco-conscious decisions.
Recyclability and Sustainability of Insulated Siding Materials
The recyclability and sustainability of insulated siding materials vary considerably. Some options, such as fiber cement siding, offer good recyclability potential, while others, like vinyl, may have lower recycling rates and potentially contribute to landfill waste. Choosing materials with high recycled content or those that are themselves recyclable significantly reduces the environmental burden. For example, some manufacturers use recycled materials in their insulated siding products, demonstrating a commitment to sustainable practices.
This reduces the demand for virgin materials and minimizes the environmental impact of extraction and processing.
Contribution to Reducing Carbon Emissions
By reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling, insulated siding directly contributes to lowering greenhouse gas emissions. The extent of this reduction depends on factors like the climate, the home’s insulation levels, and the efficiency of the heating and cooling systems. However, even a modest improvement in energy efficiency can lead to substantial carbon emission reductions over the lifespan of the siding.
For instance, a home retrofitted with insulated siding in a cold climate might see a considerable decrease in its natural gas consumption for heating, leading to a significant reduction in methane emissions. In warmer climates, reduced reliance on air conditioning translates to lower electricity consumption and therefore lower carbon emissions associated with power generation.
Examples of Environmentally Friendly Insulated Siding Options
Several insulated siding options stand out for their environmental friendliness. Fiber cement siding, often composed of recycled materials, offers excellent durability and requires minimal maintenance, extending its lifespan and reducing the need for frequent replacements. Certain types of engineered wood siding also incorporate recycled wood fibers, promoting sustainable forest management practices. These options represent a move towards more sustainable building materials, minimizing the environmental impact of construction and renovation.
Furthermore, the availability of recycled content in the manufacturing process of certain siding types is becoming increasingly common, providing homeowners with more eco-conscious choices.
Array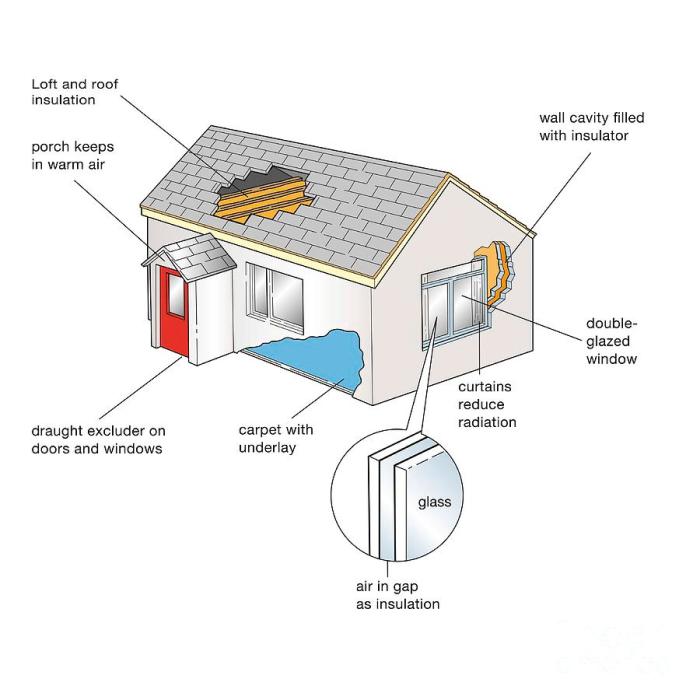
Upgrading your home’s exterior with insulated siding isn’t just about energy efficiency; it’s a significant opportunity to boost your home’s curb appeal and overall aesthetic value. The right siding choice can dramatically transform the look and feel of your property, adding value and enhancing your enjoyment of your home. Choosing wisely means considering color, texture, and how the siding complements your home’s architectural style.Insulated siding offers a wide array of options to personalize your home’s exterior.
Different materials, colors, and textures create diverse visual effects, allowing homeowners to express their personal style and enhance their property’s market value. The impact of these choices is significant, influencing everything from the overall feeling of the home to its perceived value.
Color and Texture Choices Impact on Appearance
Color is a powerful tool in home aesthetics. A light-colored siding, such as a creamy white or soft beige, can make a home appear larger and brighter, particularly effective for smaller homes or those in shaded areas. Darker colors, conversely, can create a more dramatic and sophisticated look, ideal for larger homes or those with strong architectural features. Texture adds another layer of visual interest.
Smooth siding offers a clean, modern look, while textured siding, mimicking wood grain or stone, can add warmth and character. For example, a home with a rustic design might benefit from siding with a pronounced wood-grain texture, while a contemporary home might be better suited to smooth, sleek panels. The interplay of color and texture allows for a wide range of styles, from classic to modern, creating a unique and personalized look.
Choosing Insulated Siding to Complement Architectural Styles, Insulated Siding Key to Energy-Efficient Homes
The selection of insulated siding should harmonize with the existing architectural style of the home. A Victorian home, with its intricate detailing, might be beautifully complemented by vinyl siding that mimics the look of clapboard, perhaps in a muted, historically accurate color palette. A Craftsman-style home, known for its horizontal lines and natural materials, could be enhanced with fiber cement siding that replicates the appearance of wood shingles.
Modern homes, characterized by clean lines and minimalist design, might look best with smooth, contemporary-looking vinyl or engineered wood siding in neutral tones. Matching the siding to the architectural style ensures a cohesive and visually appealing result.
Visual Representation of Insulated Siding Styles on Various Home Types
Imagine a quaint Cape Cod home, its white clapboard siding replaced with a creamy-yellow vinyl option with a subtle texture. The change instantly brightens the exterior, enhancing the home’s charming character. Next, picture a sprawling ranch-style house clad in dark gray fiber cement siding, its smooth surface reflecting the modern design of the home. The contrast between the dark siding and lighter trim accentuates the architectural lines.
Finally, envision a stately colonial home, its brick facade accented by elegant, dark brown insulated vinyl siding on the dormers and upper stories. The contrast creates a visually stunning effect, adding sophistication and depth. These examples demonstrate how the right insulated siding can significantly improve the aesthetics of various home types.
Upgrading to insulated siding isn’t just about saving money on energy bills; it’s about investing in a more comfortable, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing home. From the initial cost analysis to the long-term energy savings and environmental benefits, the advantages are undeniable. By understanding the different types of insulated siding, their installation, and maintenance requirements, you can make an informed decision that maximizes both your home’s value and its environmental impact.
So, are you ready to make your home more energy-efficient and stylish? Let’s get started!
Detailed FAQs
What is the lifespan of insulated siding?
The lifespan varies depending on the material; vinyl siding can last 20-50 years, fiber cement 50-80 years, and metal siding even longer, potentially exceeding 50 years with proper maintenance.
Can I install insulated siding myself?
While DIY is possible for some, professional installation is generally recommended for optimal results and warranty coverage. The process can be complex and requires specific tools and expertise.
Does insulated siding add value to my home?
Yes, significantly. Energy-efficient upgrades are highly desirable, increasing your home’s resale value and attracting environmentally conscious buyers.
How does insulated siding affect home insurance?
Some insurance companies offer discounts for homes with energy-efficient features like insulated siding, as it reduces the risk of damage from extreme weather.
Is insulated siding suitable for all climates?
Yes, different types of insulated siding are designed for various climates, offering protection against extreme heat, cold, and moisture. Choosing the right material for your region is crucial.